Greenhouse gases definition science 179786
Many chemical compounds in the atmosphere act as greenhouse gases These gases allow sunlight (shortwave radiation) to freely pass through the Earth's atmosphere and heat the land and oceans The warmed Earth releases this heat in the form of infrared light (longwave radiation), invisible to human eyes1 Some of theMuch like the glass of a greenhouse, gases in Earth's atmosphere sustain life by trapping the sun's heat These "greenhouse gases" allow the sun's rays to pass through and warm the planet but prevent this warmth from escaping the atmosphere into space Without them, Earth would be too cold to sustain life as we know it greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases

Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
Greenhouse gases definition science
Greenhouse gases definition science-Global warming is happening now, and scientists are confident that greenhouse gases are responsible To understand what this means for humanity, it is necessary to understand what global warming is, how scientists know it's happening, and how they predict future climateGreenhouse effect definition, an atmospheric heating phenomenon, caused by shortwave solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth's atmosphere but longerwavelength heat radiation less readily transmitted outward, owing to its absorption by atmospheric carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, and other gases;




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases (ie, greenhouse gases) in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directionsPart of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming itAbstract The morphology of CeO2 exhibited significant effect on the exposed crystal planes and oxygen vacancy concentration, resulting in the enhancement of lowtemperature catalytic activity of Ni/CeO2 catalyst for CO2 methanation © 21 Society of Chemical Industry and John Wiley & Sons, Ltd AbstractGreenhouse gases Sources As greenhouse gases are essential for the existence of life, they are present in the atmosphere in a trace amount Natural sources of GHGs are volcanos, respiration by living organisms, decay and combustion of organic matter, etc The amounts of GHGs are balanced in the atmosphere naturally by many physical, chemical
Gases like water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane, and chlorofluorocarbons primarily contribute to the greenhouse effect These gases are called greenhouse gases The five major greenhouse gases are Water Vapor Contributes about 36 to 70 percent of the greenhouse effect on Earth It is the most abundant greenhouse gas in the Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from rivers and lakes have been shown to significantly contribute to global carbon and nitrogen cycling In spatiotemporalvariable and humanimpacted rivers in the Greenhouse gases are components of the atmosphere that contribute to the greenhouse effect Some greenhouse gases occur naturally in the atmosphere, while others result from human activities such
Find my revision workbooks here https//wwwfreesciencelessonscouk/workbooksIn this video, we look at the Greenhouse Effect We explore how this takes plaThus, the rising level of carbon dioxide is viewedDefine greenhouse gas greenhouse gas synonyms, greenhouse gas pronunciation, greenhouse gas translation, Under new EPA regulations, the permits would also apply to greenhouse gas emissions, which scientists say are warming the planet, with devastating effects




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica
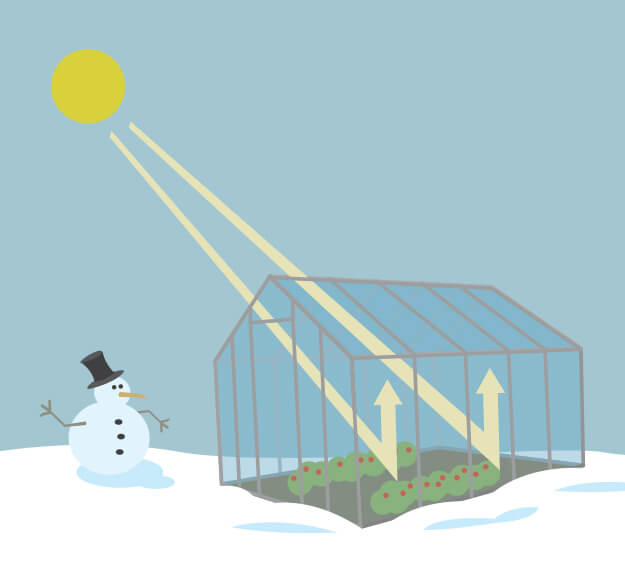
A greenhouse gas is a gas that absorbs infrared radiation and radiates heat in all directions Greenhouse gases in the earth's atmosphere absorb IR from the sun and release it Some of the heat released reaches the earth, along with What are "greenhouse gases?" The transparent windows of a greenhouse (or a car parked in the sunlight) transmit the warming visible rays of the sun, prevent the resulting warm air from leaving, and hence maintain a warmer environment inside than outside the structureThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist




Climate Change And Impacts Accelerate World Meteorological Organization




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxidesGreenhouse effect Noun phenomenon where gases allow sunlight to enter Earth's atmosphere but make it difficult for heat to escape greenhouse gas Noun gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, warming the atmosphere solar energyACS Climate Science Toolkit Greenhouse Gases Temperature is a measure of the average energy of molecular motion in a sample of matter to and fro translation, intramolecular vibration (and lattice vibration in solids), and rotation (both entire molecules and intramolecular portions)
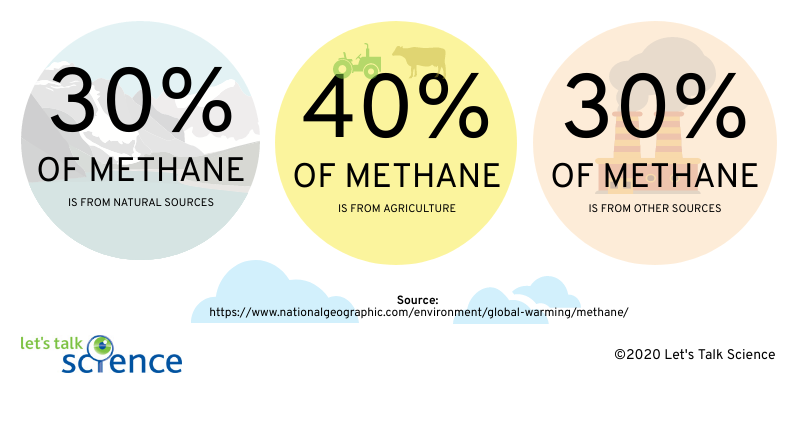



Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science



What Does Greenhouse Gases Mean Definition Of Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Gases Stands For Carbon Dioxide And Other Gaseous Emissions Resulting From Human Activity That Cause Heat To Be Trapped In
Methane gas produced by livestock is a very potent greenhouse gas, with molecules that trap far more heat in our atmosphere than carbon dioxide When methane is burned, carbon dioxide and water vapor are released into the atmosphere, but these vapors have a relatively benign impact on global warming when compared to the release of methane, had it not been used as fuelWhat are greenhouse gases?However, scientists can make estimates about future population growth, greenhouse gas emissions, and other factors that affect climate They can enter those estimates into computer models to find out the most likely effects of global warming The IPCC predicts that greenhouse gas emissions will continue to increase over the next few decades




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube




Greenhouse Gas Ghg Meaning And Several Examples
Greenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that trap heat The greenhouse effect is the term scientists use to describe the trapping of the sun's energy by Definition & Facts 456Definition of greenhouse gas any of various gaseous compounds (such as carbon dioxide or methane) that absorb infrared radiation, trap heat in the atmosphere, and contribute to the greenhouse effect Water vapor is an important gas for the study of climate and weather because of its role as a natural greenhouse gas as well as its relationship to clouds and precipitation Greenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor;
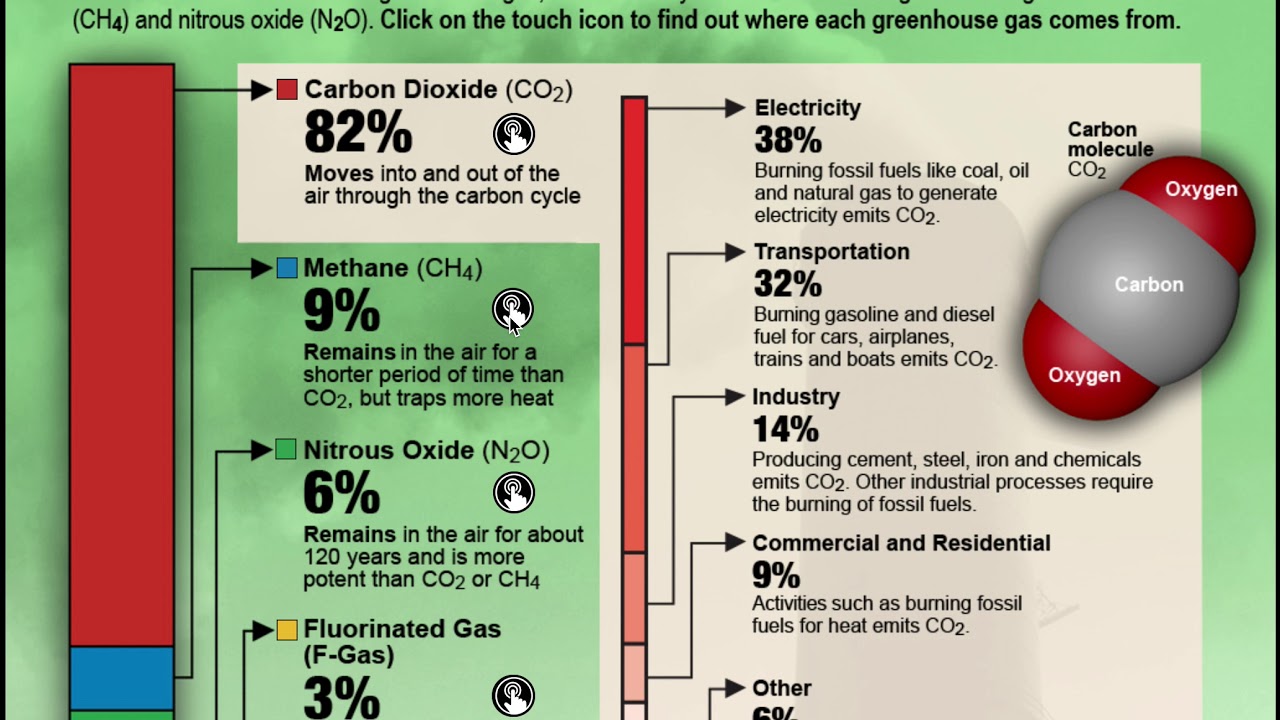



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some ofGreenhouse gas definition, any of the gases whose absorption of solar radiation is responsible for the greenhouse effect, including carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, and the fluorocarbonsGreenhouse Gases CHAPTER 4 Why some gases are greenhouse gases, but most aren't, and some are stronger than others About Gases The layer model is what is called an idealization of the real world It has the essential ingredient of the greenhouse effect, but it is missing numerous things that are important in the real atmosphere



Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gas (GHG) Earth Science any of the gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of infrared radiation emitted by the earth's surface, the atmosphere, and clouds The greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere , the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it Greenhouse gases vary in not only their sources and the measures needed to control them, but also in how intensely they trap solar heat, how long they last once they're in the atmosphere, and how they react with other gases and ultimately get flushed out of the air




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Cap And Trade What Does It Mean For
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the largest effectDefine greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, The trapping of the sun's radiation in the Earth's atmosphere due to the presence of greenhouse gases The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Larger image to save or print Gases that trap heat in the atmosphere are called greenhouse gases This section provides information on emissions and removals of the main greenhouse gases to and from the atmosphere For more information on the other climate forcers, such as black carbon, please visit the Climate Change Indicators Climate Forcing page




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science



Global Warming
A greenhouse gas is any gaseous compound in the atmosphere that is capable of absorbing infrared radiation, thereby trapping and holding heat in the atmosphere By increasingGreenhouse effectIn a greenhouse, the sun's heat can come in but cannot go out The trapped heat warms the greenhouse This trapped heat helps in controlled Greenhouse effect definition is warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to




What Is Greenhouse Gas Definition Causes Effects Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
A greenhouse gas is simply any atmospheric gas that traps heat within the atmosphere These gases allow sunlight to pass through2 days ago Greenhouse gases Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb heat energy and prevent it escaping into spaceThe Science of Greenhouse Gases and the Greenh ouse Effect The author's academic career spans over 40 years working mostly in highresolution gasphase molecular spectroscopy,




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect What Is It Definition And Role In Global Warming
Greenhouse gases are those gaseous constituents of the atmosphere, both natural and anthropogenic, that absorb and emit radiation at specific wavelengths within the spectrum of infrared radiation emitted by the Earth's surface, the atmosphere and clouds This property causes the greenhouse effect Water vapour (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrous oxide (N2O),Greenhouse gases (GHG) are gaseous compounds that can emit ultraviolet radiation within a certain thermal infrared range 76 Greenhouse gases retain high temperatures in the lower atmosphere, thus allowing less heat to escape back to space This subsequently results in the greenhouse effect and global warmingGreenhouse gases are certain gases in the atmosphere (water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane, for example) that trap energy from the sun Without these gases, heat would escape back into space and Earth's average temperature would be about 60º F colder




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




What Are Greenhouse Gases Lesson For Kids Study Com
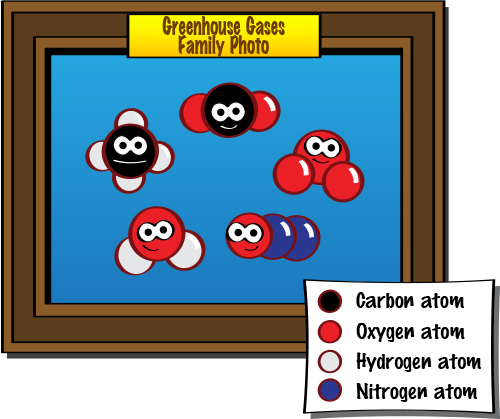



Greenhouse Effect Keeping The Balance Nasa Climate Kids



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Global Warming Green House Effect Ozone Layer Video For Kids Youtube
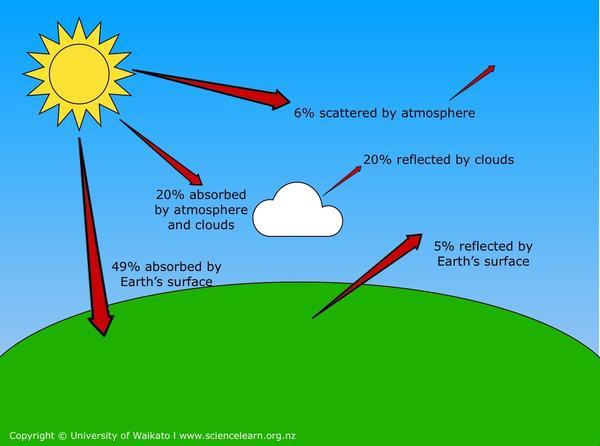



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




Food Production Is Responsible For One Quarter Of The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Science Doodle Note By Mrs Brosseau S Binder



Economic Approaches To Greenhouse Warming




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Pick A Science Word And Write The Definition Chapter 15 Or Ppt Download




Emissions Sources Climate Central




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Lesson For Kids Study Com




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization
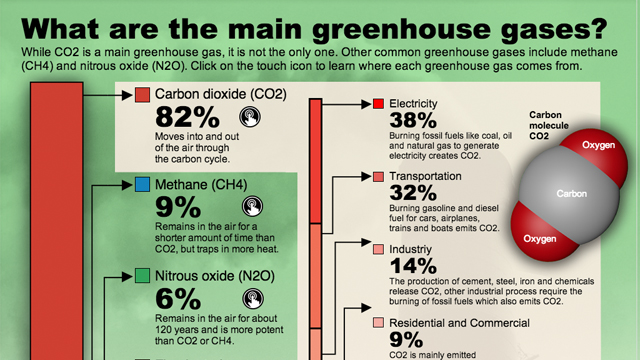



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society



1




What Are Greenhouse Gases David Suzuki Foundation




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
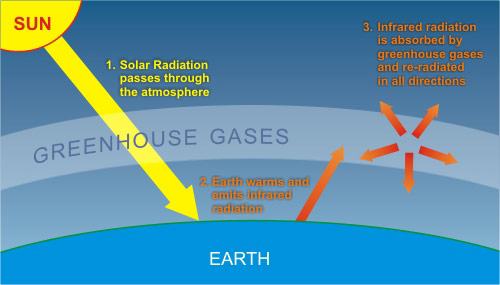



How Do We Know More Co2 Is Causing Warming




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Which Gases Are Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society
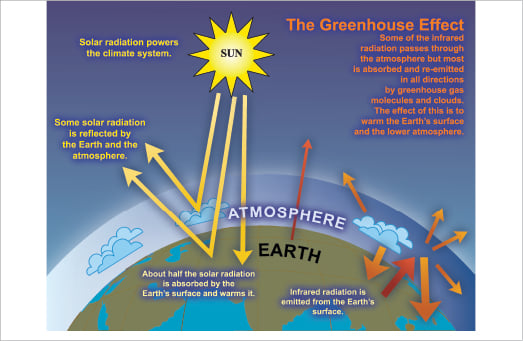



Faq 1 3 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



The Greenhouse Effect



Greenhouse Gases




What Is Nitrous Oxide And Why Is It A Climate Threat Inside Climate News




The Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gasses




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
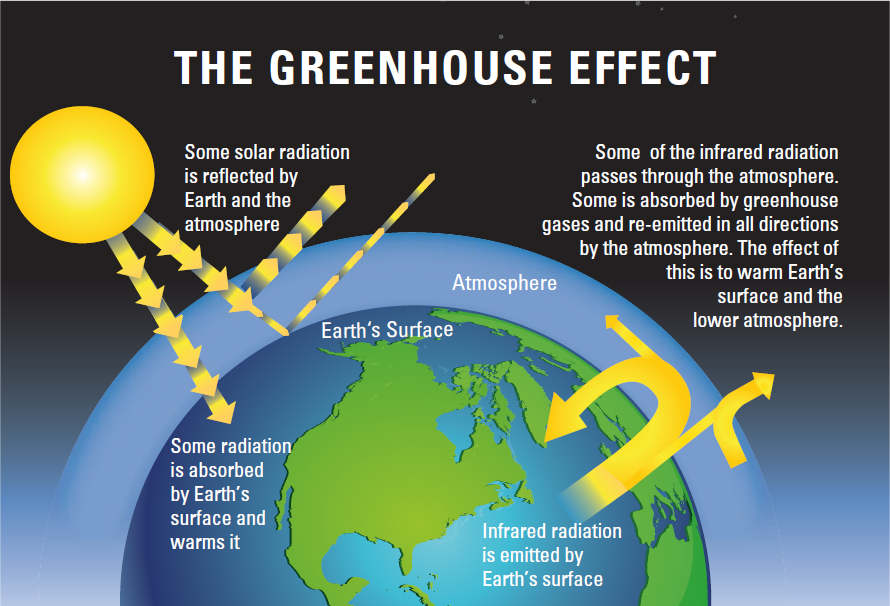



The Basics Of Climate Change Climate Change Evidence And Causes Update The National Academies Press




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate



Methane Emissions In The Oil And Gas Industry American Geosciences Institute




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
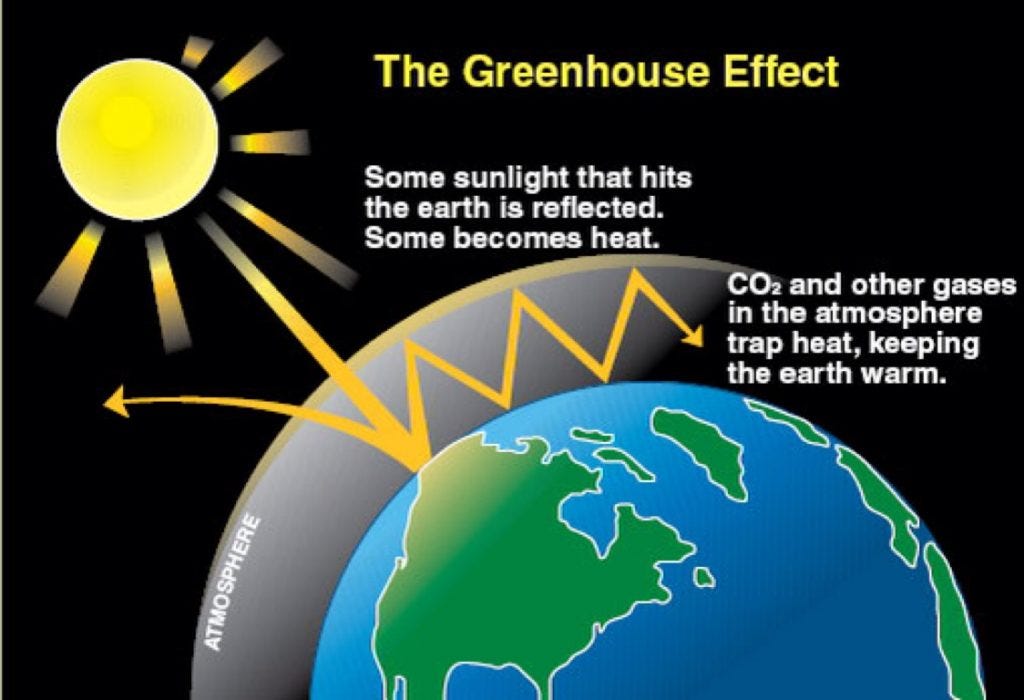



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium



Meet The Greenhouse Gases Nasa Climate Kids




Properties Of Greenhouse Gases




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



The Greenhouse Effect




What Are Greenhouse Gases Lesson For Kids Study Com




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Greenhouse Gas Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia
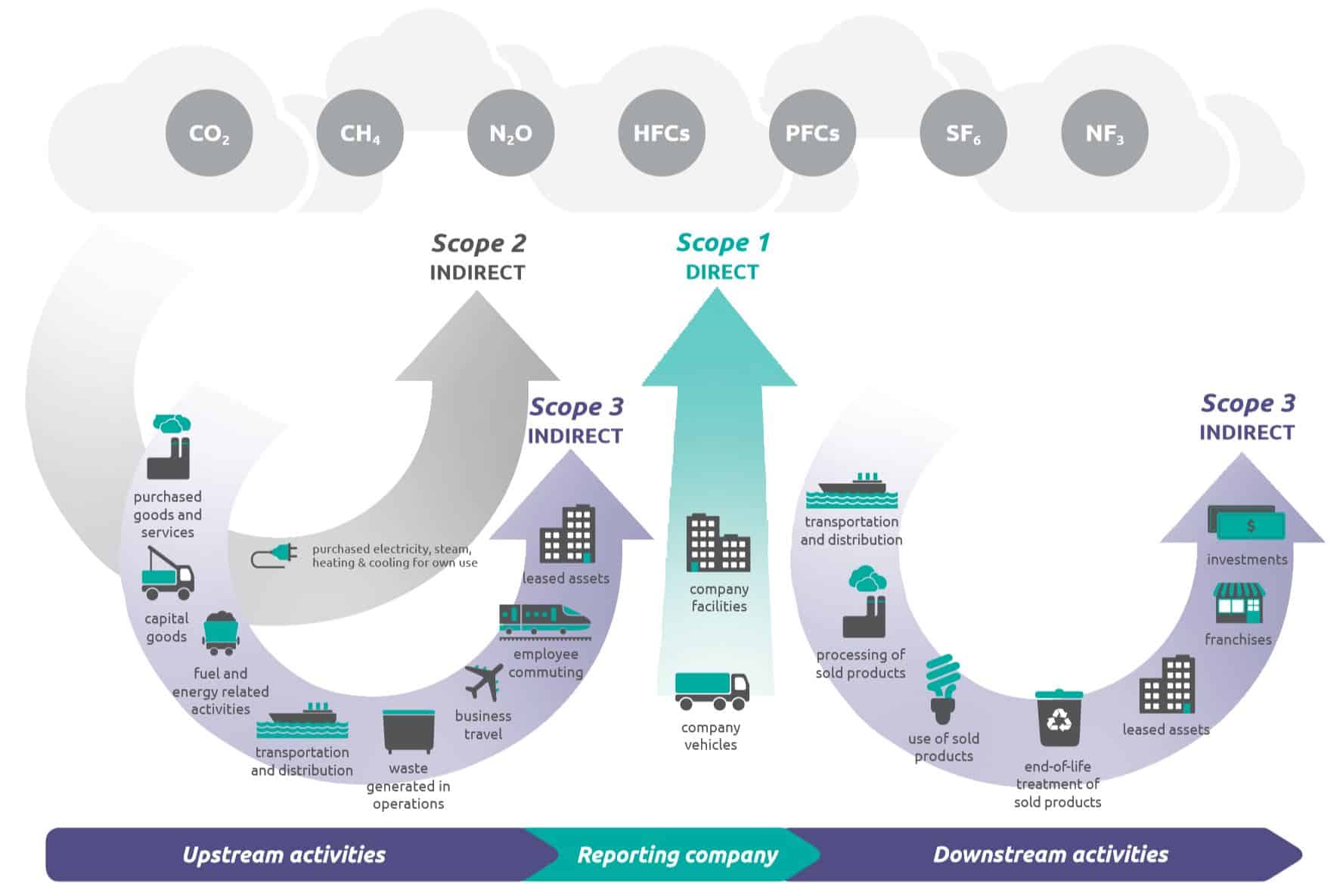



What Is The Difference Between Scope 1 2 And 3 Emissions Compare Your Footprint



Global Warming Images




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students
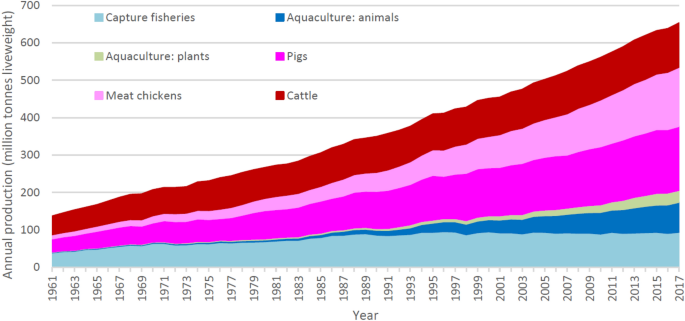



Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Global Aquaculture Scientific Reports
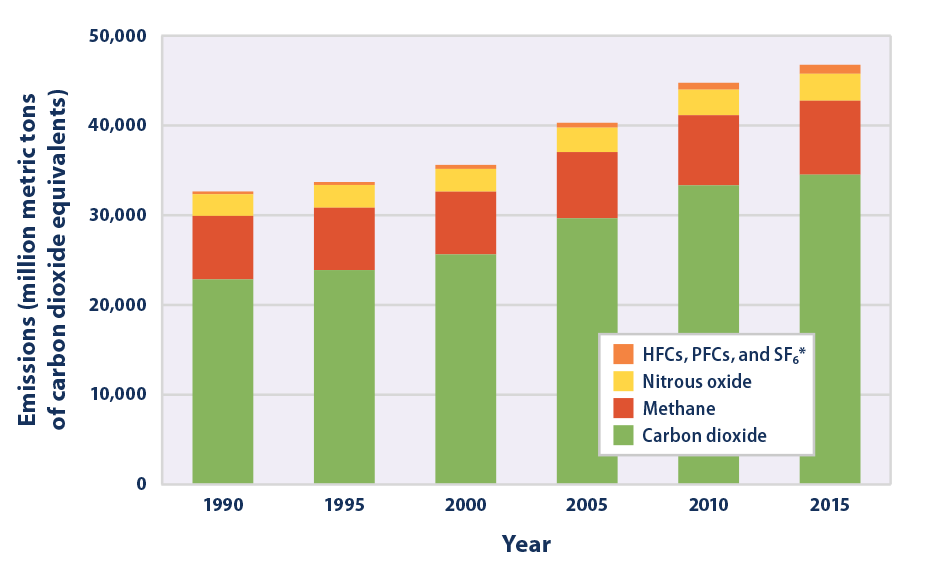



Climate Change Indicators Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
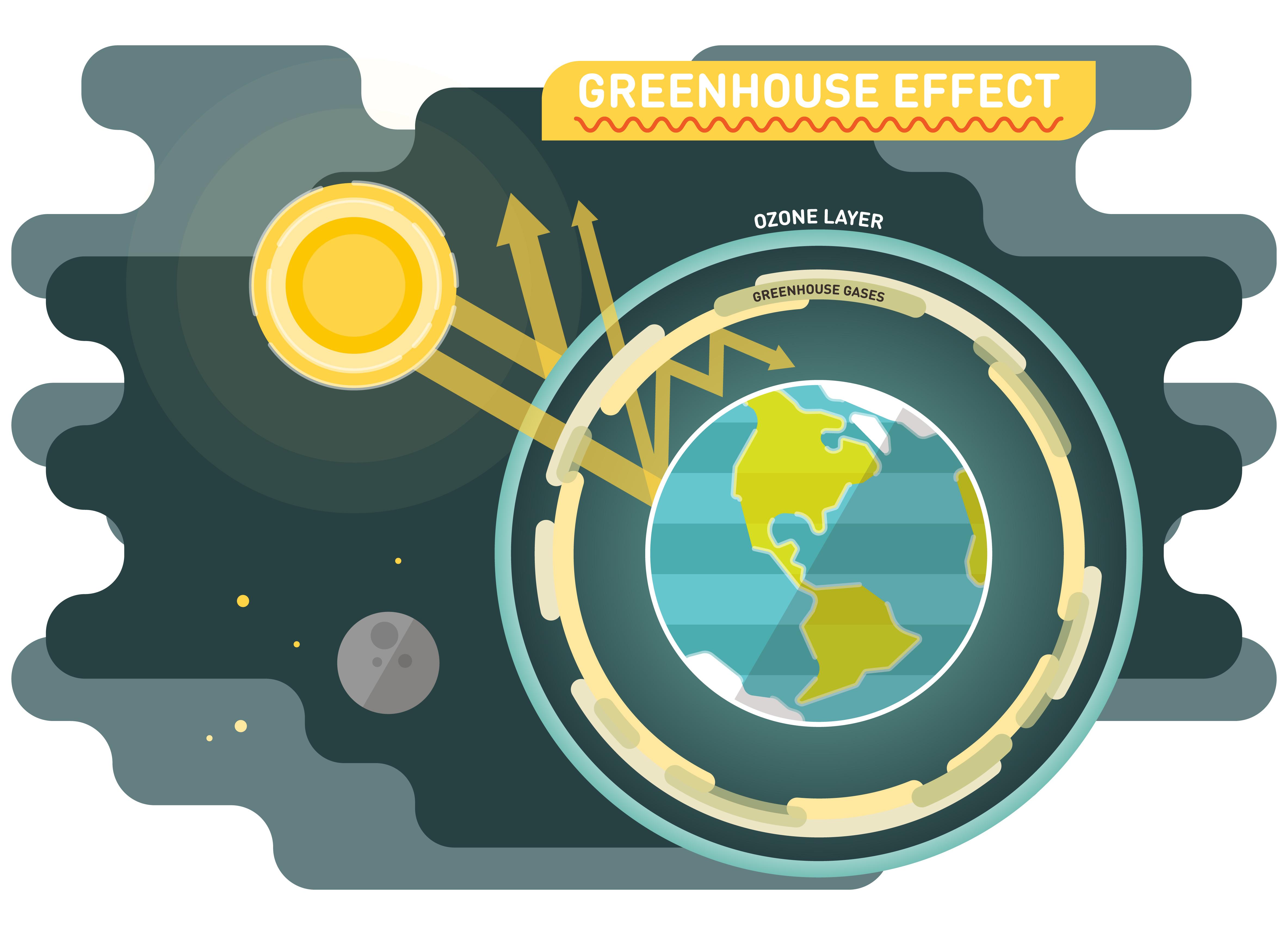



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Weatherquestions Com What Is The Greenhouse Effect What Are Greenhouse Gases



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Causes Of Climate Change




Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Gases Effect On Climate U S Energy Information Administration Eia
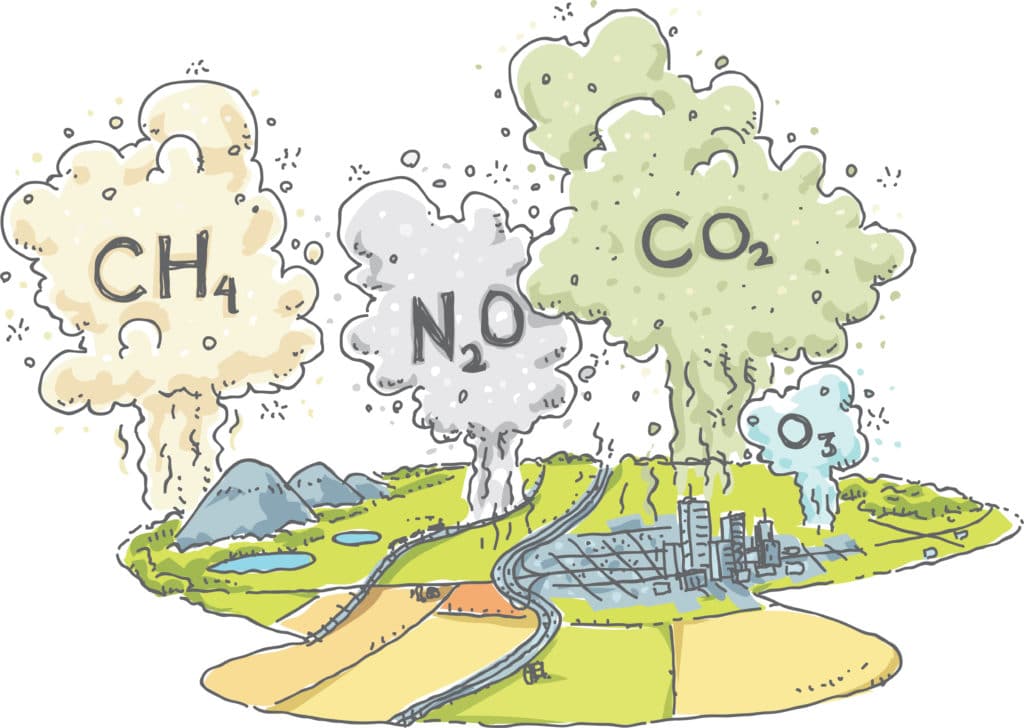



Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science
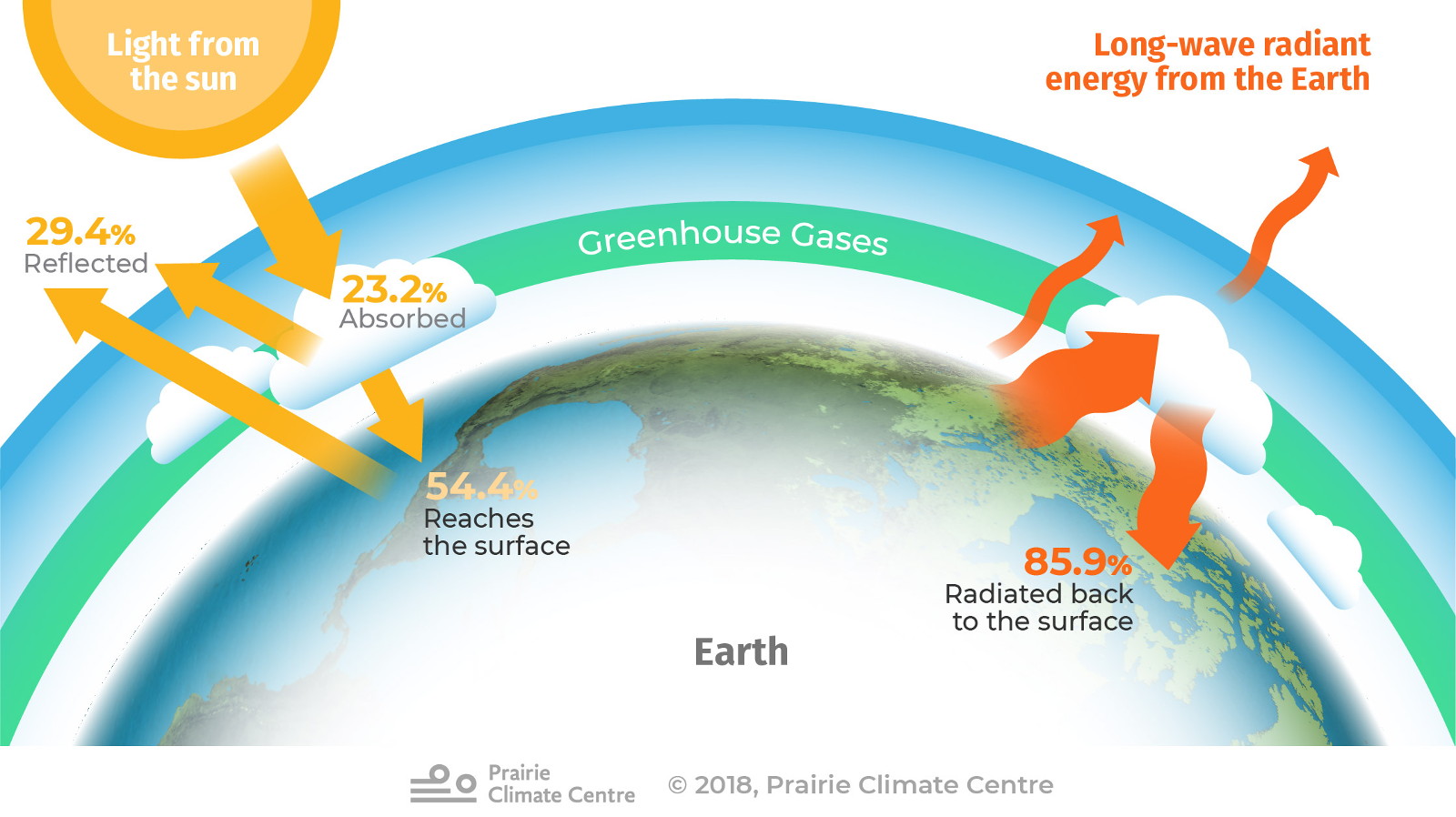



Greenhouse Gases Climate Atlas Of Canada




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Environment For Kids Global Warming




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gas Definition Emissions Greenhouse Effect Britannica




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
コメント
コメントを投稿